BREAKLS带断点的最小二乘分析方法
基本普通最小二乘法假设模型的参数不随观测值的变化而变化。尽管这种假设。结构的变化,以及样本区间参数的变化 ,在应用时间序列分析中起着重要的作用。
因此,有大量的研究针对回归方程中参数结构变动的问题。EViews 8提出了结构变动的线性回归估计工具。在Bai (1997), Bai and Perron (1998)中的断点都是已知,先前指定的。
一、Estimating Least Squares with Breakpoints in EViews
案例所需数据介绍,本节以hansen_jep为例,具体数据如下:
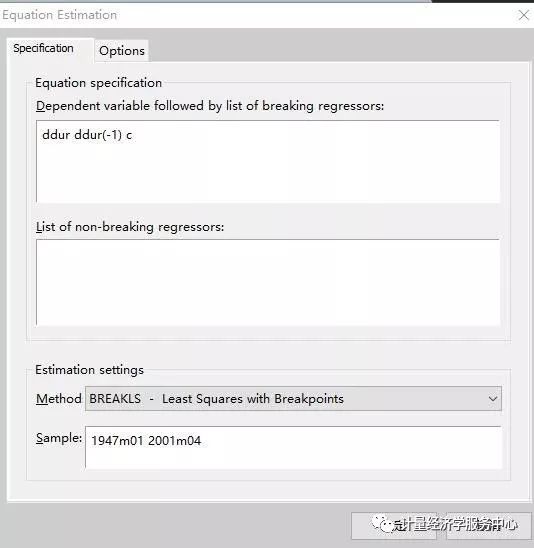
要估计一个具有断点的最小二乘方程,请选择Object/New Object….../ Equation or Quick/Estimate Equation,或者从EViews主菜单中选择BREAKLS - Method下拉菜单中带有断点的最小二乘法,或者在命令窗口中简单输入关键字BREAKLS:
接下来,单击Options选项卡,显示计算系数协方差矩阵、断点说明、权重和系数名的附加设置。
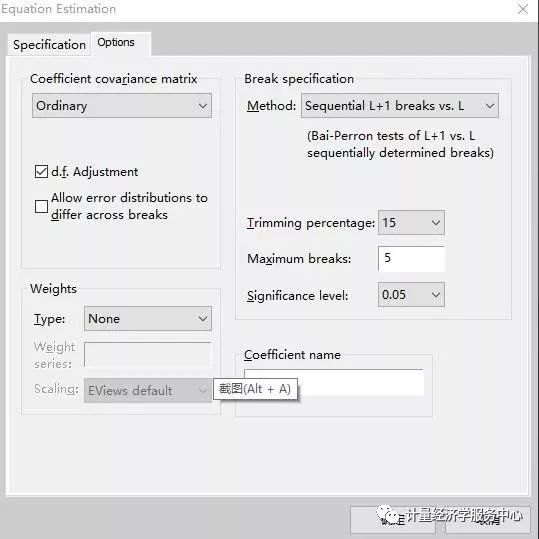
Break Specification包括如下选项:
The Break specification section of the dialog contains a Method drop-down where you may specify the type of test you wish to perform. You may choose between:
• Sequential L+1 breaks vs. L
• Sequential tests all subsets
• Global L breaks vs. none
• L+1 breaks vs. global L
• Global information criteria
• Fixed number - sequential
• Fixed number - global
• User-specified
这些选项在结构突变检验章节将再次介绍。为了说明断点方程估计的输出,我们使用Han- sen’s (2001)劳动生产率的例子。Hansen的示例使用了1947年2月至2001年4月美国劳动生产率在制造业耐用品行业的测量。工业生产指数与每周平均工时之比增长率。
我们估计一个断点模型,使用DDUR与DDUR(-1)和一个常数的回归。输出如下:
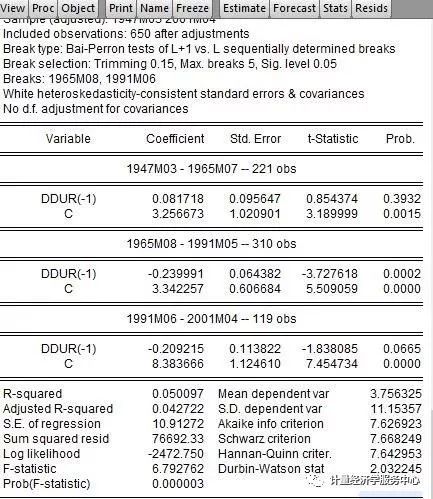
Breakpoint Specification View显示一个断点回归的总结,该方法用于确定断点。输出的顶部显示断点摘要以及剩下的部分显示了断点确定的中间结果:
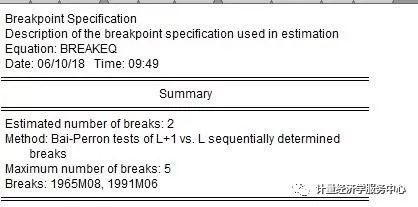
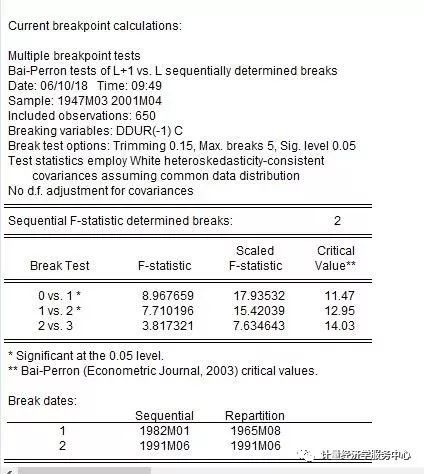
为了说明这些工具在实践中的使用,我们采用了美国出口实际利率的数据(from Garcia and Perron (1996) that is used as an example by Bai and Perron (2003a).)
选择对象/新对象…从主菜单中 或在命令行中输入命令断点并单击enter。
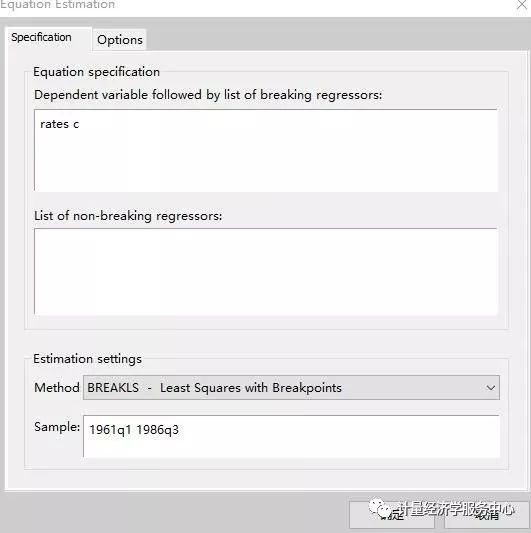
Next, click on the Options tab and specify HAC (Newey-West) standard errors, check Allow error distributions to differ across breaks, choose the Bai-Perron Global L breaks vs. none method using the Unweighted-Max F (UDMax) test to determine the number of breaks, and set a Trimming percentage of 15, and a Significance level of 0.05.
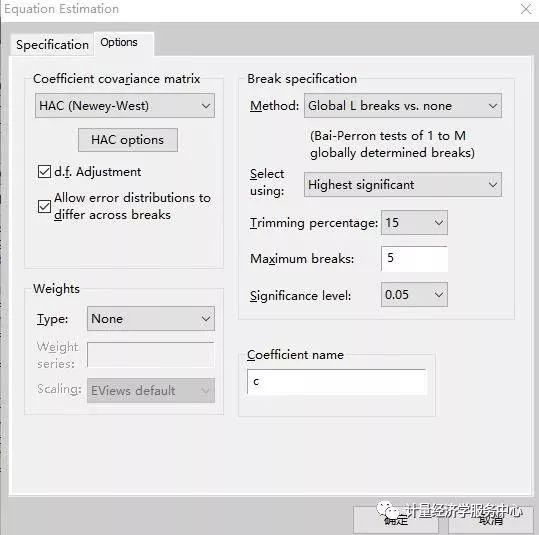
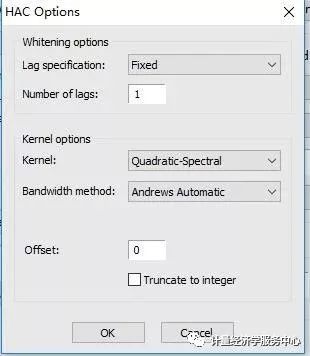
Lastly, to match the test example in Bai and Perron (2003a), we click on the HAC Options button and set the options to use a Quadratic-Spectral kernel with Andrews automatic bandwidth and single pre-whitening lag:
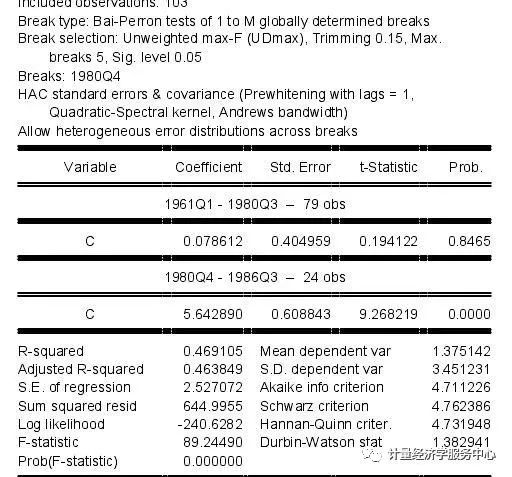
输出结果为:
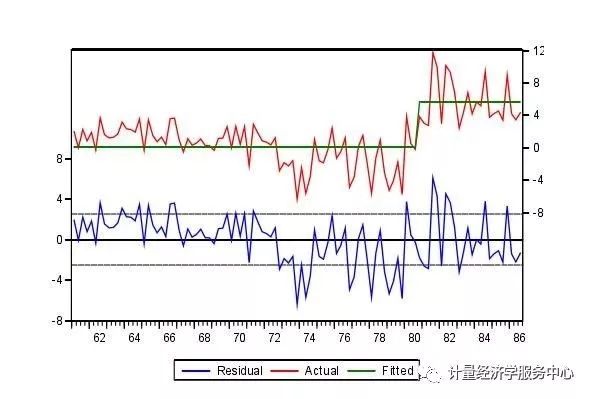
点击视图/实际,拟合,剩余/实际,拟合,残差图,在原始序列和残差的旁边,查看样本内的拟合数据: